Apache Guacamole is a client-less remote desktop gateway. It supports protocols like VNC, RDP, and SSH. Once Guacamole is installed on a server, all you need to access your desktops is a web browser.
Guacamole can be deployed using Docker, removing the need to build guacamole-server from source or configure the web application manually. The Guacamole project provides officially-supported Docker images for both Guacamole and guacd which are kept up-to-date with each release.
Here I will explain how to run Guacamole with two containers, guacd and guacamole. PostgreSQL will be used for authentication. Please note that PostgreSQL will not be running in a container.
guacamole/guacd
Provides the guacd daemon, built from the released guacamole-server source with support for VNC, RDP, SSH, telnet, and Kubernetes.
guacamole/guacamole
Provides the Guacamole web application running within Tomcat 8 with support for WebSocket. The configuration necessary to connect to guacd, MySQL, PostgreSQL, LDAP, etc. will be generated automatically when the image starts based on Docker links or environment variables.
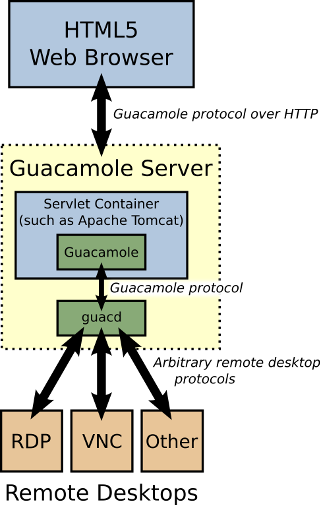
Guacamole architecture
Run guacd container
In order to run guacd container
docker run --name guacd -d -p 4822:4822 guacamole/guacd
PostgreSQL authentication setup
To create the guacamole database you need to run the following SQL commands
CREATE DATABASE guacamole;
CREATE USER guacamole WITH PASSWORD 'ChangeMePlease';
GRANT SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO guacamole;
GRANT SELECT,USAGE ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA public TO guacamole;
To generate PostgreSQL initialization script you need to run the following command
docker run --rm guacamole/guacamole /opt/guacamole/bin/initdb.sh --postgres > initdb.sql
Once the guacamole database and user are created, you can run the guacamole initialization script. It will create the data structures required for Guacamole
psql -U guacamole -f initdb.sql
Run guacamole container
At this point you will have everything that is required to run the guacamole container
docker run --name guacamole \
--link guacd:guacd \
--add-host postgres:192.168.1.10 \
-e POSTGRES_HOSTNAME=postgres \
-e POSTGRES_DATABASE='guacamole' \
-e POSTGRES_USER='guacamole' \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD='ChangeMePlease' \
-d -p 8180:8080 guacamole/guacamole
At this point you will have a working Guacamole set of containers that are able to authenticate to a PostgreSQL database. You can login to Guacamole with your web browser to your server URL, for example http://localhost:8180 (note that I exposed port 8180, as 8080 is already taken in my server). The default user is guacadmin with password guacadmin. You should log in and change your password immediately.
In case you need to troubleshoot your guacamole container, you can
docker logs some-guacamole
PostgreSQL Troubleshooting
If you face issues connecting to your PostgreSQL instance, please make sure that:
- your postgresql.conf file line listen_addresses is set to
listen_addresses = '*'
- your pg_hba.conf file is allowing network access (you choose what works best for your particular case)
# this will allow to access the docker host
host all all 172.17.0.1/16 md5
# this will allow access from any address your PostgreSQL server is listening
host all all 0.0.0.0/16 md5
You need to reload your PostgreSQL server so changes take place
sudo systemctl reload postgresql.service
Apache Proxy
The apache configuration to reverse proxy Guacamole containers from the localhost is (remember that I'm using port 8180, adjust host and port based on your own needs)
<Location /guacamole/>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
ProxyPass http://localhost:8180/guacamole/ flushpackets=on
ProxyPassReverse http://localhost:8180/guacamole/
</Location>
IMPORTANT If the option flushpackets=on is not specified, Guacamole may not work.
You need to setup mod_proxy_wstunnel as well
<Location /guacamole/websocket-tunnel>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
ProxyPass ws://localhost:8180/guacamole/websocket-tunnel
ProxyPassReverse ws://localhost:8180/guacamole/websocket-tunnel
</Location>
The Location section for /guacamole/websocket-tunnel must be placed after the Location section for the rest of Guacamole.
Once your apache configuration is updated you need to reload it.
sudo systemctl reload apache2.service